When metal components are created, they have various ways of shaping the metal. Two common techniques are foundry and forging. A foundry melts metal like lava and then pours it into a mold to create a shape like using a cake pan.
Forging is different from foundry. It squishes and molds solid metal with large machines, like a giant hammer pounding clay. Both processes are beneficial, but they serve different purposes. Foundry is excellent for creating intricate shapes, and forging makes metal extremely strong.
Why it’s Important to Know the Difference between Forging and Foundry
Knowing the difference between forging and foundry allows individuals to choose the best method of making strong and safe metal components. If they choose an inappropriate method, the component can be destroyed or too expensive.
Forging is fine if we require strong components, for instance, in planes or automobiles. Foundry is preferable when we require producing odd shapes. Gaining an insight about the difference between forging and foundry lets constructors make equipment, machinery, and vehicles more efficient.
What Is a Foundry Process?
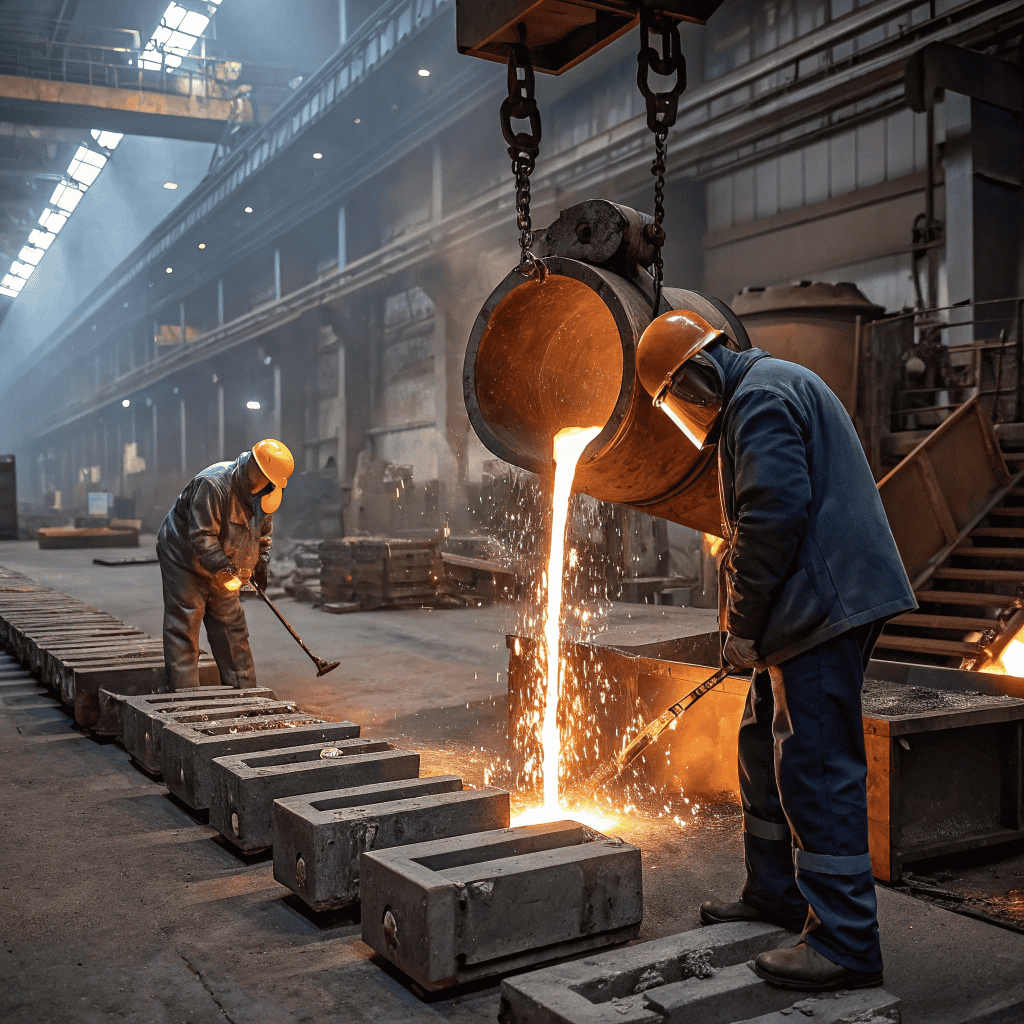

The foundry process is when we heat metal until it turns into hot liquid, then pour it into a mold. Once it cools and becomes hard again, it has the shape of a mold. It is just like pouring jelly into a mold and setting it hard. The foundry is utilized to produce car parts, tools, and other machines.
Foundry / Casting
A foundry is a facility where metal pieces are made. Casting is the process by which metal is melted and poured into a mold. When metal hardens, it is hard and retains the shape of the mold. It’s similar to pouring chocolate into an interesting mold and hardens in that shape.
Explain the casting process:
Melting the Metal: We melt the metal in a furnace until it’s a hot liquid like melting ice into water.
Pouring Into a Mold: We pour the hot metal into a mold, a shape like the end piece we’re trying to make.
Cooling and Hardening: The metal is cooled in the mold. As the metal cools, it hardens again and stays in the shape of the mold.
Post-Processing: When it’s solid, we extract the part, wash it, and occasionally trim or polish it to prepare it for use.
Common casting methods
Sand Casting
Sand casting is a casting method that uses sand molds to shape and produce metal objects and components. Sand casting is one of the oldest known casting processes and is valued for its flexibility, cost-effectiveness, and ability to create complex shapes.
Investment Casting
Investment casting is a manufacturing process in which a wax pattern is coated with a refractory ceramic material. Once the ceramic coating material is dry and hardened, the wax is melted out and leaves an internal cavity the shape of the final product’s geometry.
Molten metal is poured into the cavity where the wax pattern was. The metal solidifies within the ceramic cavity, cools, and the ceramic is removed from the metal casting. The result of this process is a net to near-net precision metal component which can be used for a broad range of applications in various industries.
What Is Forging?

Forging is a method of shaping metal by striking or pushing it when it is hot or cold. Rather than melting it like in casting, we leave it solid and break it into shape with powerful machines. That makes the metal very hard from the inside, like when you pack snow tightly so you can have a snowball.
Forging is wonderful for creating strong parts used in cars, airplanes, and machinery. It is because it hardens the metal and cannot be easily broken.
Describe forging process
Heating (for Hot Forging):
The metal is first heated to a very high temperature in hot forging before being shaped. This causes the metal to become softer and more manageable. The heat makes it more pliable to bend and form. As it is something that is necessary for forming complex shapes.
Applying Pressure to Shape the Metal
When heated, the metal is placed between two dies or machines. The high pressure of these molds the metal into its desired shape. The pressure compresses the metal into the die’s shape.
Die Types: Open Die vs. Closed Die:
Open Die: The metal is formed using pressure. But can spread out and alter in various directions, providing greater design versatility.
Closed Die: Metal is forced into a close-fitting mold such that finer details. The shapes can be made, helping to produce accurate duplicate parts.
Overview of cold vs hot forging
Cold Forging
Cold forging is performed at room temperature; hence, the metal hardens and strengthens. The metal doesn’t have to be heated, and the process may be faster. But it’s good for small or simple parts.
Hot Forging
Hot forging uses heat to soften and melt the metal so that it may be molded. It is appropriate for producing large or complicated pieces. The heat softens the metal and makes it easier to mold against pressure.
The two processes create strong, tough pieces of metal based on the quantity, complexity, and size of the material required.
Key Differences Between Forging and Foundry

| Feature | Forging | Foundry (Casting) |
| Process | Shaping metal is done with the application of pressure. | Melts metal and shapes into the mold. |
| Temperature | Hot or cold, depending on the process. | Melts metal to liquid. |
| Strength | Creates stronger, enduring parts with a compacted grain structure. | Parts can be weaker depending on the cooling rates. |
| Complexity of Shape | Less suitable for intricate shapes or those requiring strength. | Best for complicated or detailed shapes. |
| Material Waste | Typically, less waste is produced. | This will create more waste depending on the molding shape. |
| Speed | Typically, it is faster for basic parts. | It may take longer to set up and cool the mold. |
| Applications | Automotive crankshaft (forged), aerospace components (forged). | Engine block (cast), decorative parts (cast). |
Real-life Applications
In forging, metal is compressed and heated to shape, making the part extremely strong. A perfect example of a forged part is that of the car’s crankshaft. It has to be hard and robust to handle the pressure of an engine. Forging strengthens the metal’s grain structure. So, forging would be suitable for parts that must be harder.
Forging must melt the metal and pour it into a mold. An example of a cast part is an engine block. Casting is used because it can accommodate more complex geometries. Like the minute channels in an engine block, which would be difficult to forge.
When to Use Forging or Foundry?
When one needs to decide between forging and casting, it simply depends on what the part needs. Forging is best when you want to create a strong and durable part, such as in the crankshaft of a car. It’s ideal for simple shapes when they need to be strong.

Casting is ideal for producing parts of complex shapes, such as engine blocks. Casting is ideal for creating complex designs, but the parts will not be as strong as forged ones. Thus, if the most critical concern is strength, then forging is best. If the shape’s intricacy is the most critical concern, then casting is best.
Criteria: Mechanical Properties, Geometry, Volume, Cost
In choosing between casting and forging, the following need to be weighed:
Mechanical Properties: Forging forms parts that are stronger. As it deforms the metal when in solid form. This strengthens the metal and can endure high stress. Casting can produce complex shapes but perhaps not as strong as forged parts.
Geometry: Casting is best for making intricate shapes and complex designs like engine blocks. Forging is best for simple shapes that must be durable, such as car components.
Volume: For low-volume production or special parts, forging is best. Casting would be best for producing large quantities of parts in a short amount of time.
Cost: Forging is costly as it requires the application of specialized tools and additional man-hours. While casting could be less costly, particularly for complicated shapes in high numbers.
Industry use cases
Aerospace: Forging is applied in the aerospace sector to produce thin, high-strength components. Some examples are airplane landing gear and engine parts. These parts must be extremely strong to resist harsh forces and temperatures. Casting is also applied to intricate components. Some are such as engine blocks, which can be cast into advanced shapes.
Automotive: Forging is used by automobile makers in key components such as crankshafts and connecting rods. It must endure heavy loads. Casting is commonly used for large components such as engine blocks and transmission housings. It’s optimally used for casting complex shapes.
Mining: Forging equipment needs sturdy forged components such as gears and shafts. They must withstand high loads. Cast components can also be utilized for non-load-bearing components such as covers and housings.
Marine: Forging is utilized in the marine sector. Like for propeller shafts and other stressed components. Casting is used for boat hulls and engine blocks. It is because it produces big, complicated shapes.
Oil & Gas: The oil and gas sector applies forging for heavy-duty components. It is for pipes and valves that must withstand high pressure. The application of parts such as pump casings also uses casting. It must be of complex form for functionality.
Advantages and Disadvantages

There are a number of points that can be considered about forging and foundry. The advantages and disadvantages of forging and foundry are given below:
Advantages of Forging:
- Strength: The forged components are extremely strong and can withstand heavy loads.
- Fatigue Resistance: They can withstand wear and tear over long periods.
- Low Porosity: Less small holes, thus stronger.
Advantages of Foundry:
- Design Flexibility: Able to make very intricate shapes that are difficult to produce by other methods.
- Complex Shapes: Excellent at producing parts with intricate designs.
- Lower upfront tooling for small batches: Producing molds, particularly for small quantities, is cheaper.
Disadvantages of Forging:
- More expensive to produce for complex shapes and small quantities.
Disadvantages of Foundry:
- Not as strong as forged components.
- It may be more porous and, thus, less durable.
Conclusion
Both forging and foundry are significant processes for shaping metal but are not identical. Squeezing and shaping the solid metal on forging presses forms a very strong material. Casting casts and melts metal and is used to produce small details. More complicated shapes of parts can be cast parts, and long-lasting parts can be forged parts.
If you have to create solid or detailed metal parts, choosing the right method is crucial. Contact Hanke Construction Machinery Manufacturing Co., Ltd for custom forging or casting assistance. We support your needs.
FAQ Section
Is forging costlier than casting?
Yes, forging is typically costlier than casting. The reason is that forging involves using specialized tools and equipment to pound or press metal into shape. It requires more labor, energy, and time. It also requires tougher materials and more careful handling.
However, forged parts are extremely hardy and long-lasting. So, the additional expense is justified. Casting is usually less expensive. It is particularly for producing large numbers of pieces at once or for pieces of intricate shapes. But the pieces will not be as durable as forged items.
Are all metals forgeable?
No, all metals are not forgeable. There are too-hard, too-brittle, or too-low-melting metals that cannot be forged easily or at all. For instance, aluminum, steel, and titanium can be forged since they can be heated and molded without destruction.
However, extremely brittle metals like cast iron can break or shatter upon pressure. So, the appropriate metal must be used for forging, depending on how strong it is, how malleable it is, and how it will respond to pressure and heat.
What are some examples of cast versus forged parts?
Here are a few examples to help you understand the difference:
Forged parts are created by hammering or pressing metal into shape. These parts are extremely strong. A good example is an automobile crankshaft or aircraft landing gear, they must be tough because they are subjected to a lot of stress.
Cast parts are produced by melting metal and pouring it into a mold. Cast parts may be more complex in design. A good example is an engine block or valve cover, which have complex designs that may be easier to produce using casting.




